
Regardless of company policies and procedures for credit collections, the risk of the failure to receive payment is always present in a transaction utilizing credit. Thus, a company is required to realize this risk through the establishment of the allowance for doubtful accounts and offsetting bad debt expense. In accordance with the matching principle of accounting, this ensures that expenses related to the sale are recorded in the same accounting period as the revenue is earned. The allowance for doubtful accounts also helps companies more accurately estimate the actual value of their account receivables.
Bad Debt Estimation
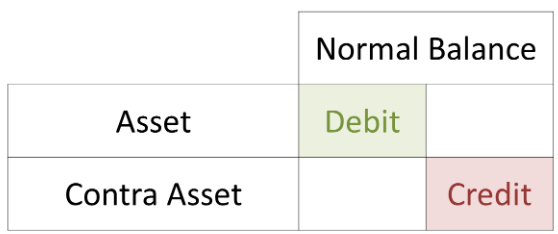
The allowance for doubtful accounts is not specifically reported, but the 10(K) reported that the allowance is immaterial to the amount. This make sense because Home Depot wouldn’t be carrying accounts receivable with long payment terms. Most accounts receivable would just be the time between purchase and credit card settlement. Learn why contra accounts, when utilized correctly along with a paired account, are a crucial component of accurate accounting and financial review. In the financial statements the asset a/c would be offset against the contra asset a/c to show the net balance.
How to Account for the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Balance sheet readers cannot only see the actual cost of the item; they can also see how much of the asset was written off as well as estimate the remaining useful life and value of the asset. This is different from the last journal entry, where bad debtwas estimated at $58,097. That journal entry assumed a zero balancein Allowance for Doubtful Accounts from the prior period. Thisjournal entry takes into account a debit balance of $20,000 andadds the prior period’s balance to the estimated balance of $58,097in the current period.
Reconciling Contra Asset Balances
Thismeans that BWW believes $22,911.50 will be uncollectible debt.Let’s say that on April 8, it was determined that Customer RobertCraft’s account was uncollectible in the amount of $5,000. There is one more point about the use of the contra account,Allowance for Doubtful Accounts. In this example, the $85,200 totalis the net realizable value, or the amount of accounts anticipatedto be collected. However, the company is owed $90,000 and willstill try to collect the entire $90,000 and not just the$85,200.
Why Do Accountants Use Allowance for Doubtful Accounts?
If the following accounting period results in net sales of $80,000, an additional $2,400 is reported in the allowance for doubtful accounts, and $2,400 is recorded in the second period in bad debt expense. The aggregate balance in the allowance for doubtful accounts after these two periods is $5,400. The sales method applies a flat percentage to the total dollar amount of sales for the period. For example, based on previous experience, a company may expect that 3% of net sales are not collectible. If the total net sales for the period is $100,000, the company establishes an allowance for doubtful accounts for $3,000 while simultaneously reporting $3,000 in bad debt expense.
When we add the balances of two of these assets together, it reflects the net book value or carrying value of the debit balance assets. Accumulated depreciation is considered a contra asset because it contains the cumulative total of all depreciation expense recognized on an asset to date. Rather than altering the original cost of the asset, it serves to reduce the asset’s value on the balance sheet, thus representing the asset’s declining value over its useful life. Notes Payable and Discount on Notes PayableFor liability accounts, such as Notes Payable, a contra account can reflect the cost of borrowing over time. A Discount on Notes Payable, for instance, accounts for the difference between the cash received and the note’s face value. If a $100,000 note is issued at a 2% discount, the Discount on Notes Payable would be $2,000, effectively reducing the liability over the note’s life until it reaches its face value at maturity.
- It may be obvious intuitively, but, by definition, acash sale cannot become a bad debt, assuming that the cash paymentdid not entail counterfeit currency.
- For example, if a piece of heavy machinery is purchased for $10,000, that $10,000 figure is maintained on the general ledger even as the asset’s depreciation is recorded separately.
- The allowance for doubtful accounts estimates the percentage of accounts receivable that are expected to be uncollectible.
- Assuming that credit is not asignificant component of its sales, these sellers can also use thedirect write-off method.
- The allowance for doubtful accounts is a contra asset because it reduces the value of the accounts receivable (AR) account on the general ledger.
The amount is reported on the balance sheet in the asset section immediately below accounts receivable. Continuing our examination of the balance sheet method, assumethat BWW’s end-of-year accounts receivable balance totaled$324,850. This entry assumes a zero balance in Allowance forDoubtful Accounts from the prior period. BWW estimates 15% of itsoverall accounts receivable will result in bad debt. Yes, allowance accounts that offset gross receivables are reported under the current asset section of the balance sheet.
By the end of 2nd-year, the machinery balance will still be $100,000, and accumulated depreciation will show $40,000. The netbook value of the machinery by the end of the first year will be $80,000 ($100,000-$20,000) and $60,000 ($100,000-$40,000) by the end of the second year. This method helps a third person identify what the book value was at the time of purchase and the remaining value of an asset.
By a miracle, it turns out the company ended up being rewarded a portion of their outstanding receivable balance they’d written off as part of the bankruptcy proceedings. Of the $50,000 balance that was written off, the company is notified that they will receive $35,000. Charlene Rhinehart is a CPA , CFE, chair of an Illinois CPA Society committee, and has a degree in accounting and finance from DePaul University. Contra accounts are confusing at first, but, with a little study, understanding them becomes second nature. Let’s go over how they work and what the main types are, and then finish with an example.
Given below are the examples of Accumulated Depreciation & Reserve/Provision for Doubtful Debts. The calculation and posting in the extract of the balance sheet are also provided. All programs require the completion of a brief online enrollment form before payment. If you are new to HBS Online, you will be required to set up an account before enrolling in the program of your choice. A balance sheet must always balance; therefore, this equation should always be true. Note that if a company believes it may recover a portion of a balance, it can write off a portion of the account.
For example, the depreciation expense recorded is a result of reducing the book value of fixed assets, and it is reported as an expense in the income statement every accounting period. This creates a direct link between the reduction of fixed asset value on the balance sheet and the recognition of expenses on the income statement. The alignment of the cost principle with expense recognition helps ensure that where do contra assets go on a balance sheet the income statement reflects accurate and periodic matching of revenues with expenses. A contra account is a negative account that is netted from the balance of another account on the balance sheet. The two most common contra accounts are the allowance for doubtful accounts/bad debt reserve, which is subtracted from accounts receivable, and accumulated depreciation, which is subtracted from fixed assets.
